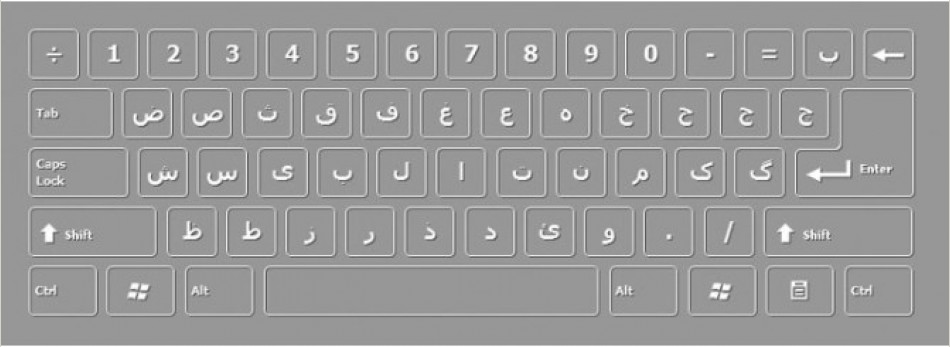
FARSI DESKTOP KEYBOARD FREE DOWNLOAD
Language:Farsi
Type: Virtual Onscreen Keyboard
Platform:
WindowsXP
Windows 7
Windows 8 (coming soon)
Windows 10 (coming soon) DescriptionReviews (0) FarsiSimilar Keyboards (6)
Farsi (Persian)
Farsi belongs to Iranian branch of Indo-European language family. Persian or Western Farsi is
spoken by about 22 million people residing in Iran. A close variant, Dari (Eastern Farsi), is
spoken by seven million people in Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan. Both varieties are also spoken
in some other countries as well [1, 2]. Figure 1 shows the language family tree of Farsi.
Indo-European
Indo-Iranian
Iranian
Western
South Western
Persian
FARSI
Language Tree Farsi of Language. Farsi has been written with a number of different scripts, including Old Persian Cuneiform,
Pahlavi, Aramaic, and Avestan. However after 642 AD Arabic script has been used for writing
Farsi. Nastalique style for Arabic script is used for writing Farsi.
Character Set and Encoding
Unicode Arabic script block from 0600-06FF is the standard character set encoding used for
Farsi. A national standard based on relevant Unicode character subset within Arabic script block
is also defined by Institute of Standards and Industrial Research in Iran (ISIRI). Earlier popular
Farsi character set used for encoding was “Iran System”. The figure below shows this character
set encoding. provides the Farsi (Persian) user with four applications of office with a Farsi (Persian) User
Interface. This white paper will show what is the benefits of Farsi (Persian) LIP, and how to install
and use it over your English Office applications.
Microsoft Platform
Microsoft Windows fonts Tahoma and Microsoft Sans Serif can be used for typing Farsi text. In
addition to this there are other Unicode Farsi fonts available, some of which have been shown in
the figure below. All these fonts follow the Naskh style of Arabic script. No Nastalique style font is
available by Microsoft. Nastalique Open Type fonts are available from other organizations, which
can be used for Persian, e.g. Nafees Nastalique
Keyboard
ISIRI has published keyboard standard ISIRI 2901:1994
Omniglot - the online encyclopedia of writing systems & languages
Persian (Fārsī/فارسی)

The Persian language has been written with a number of different scripts, including the Old Persian Cuneiform, Pahlavi, Aramaic, and Avestan, Cyrillic and Latin alphabets. After the Islamic conquest of the Persian Sassanian Empire in 642 AD, Arabic became the language of government, culture and especially religion. Modern Persian appeared during the 9th century. It is written in a version of the Arabic script and is full of words of Arabic origin. There are also two methods of writing Persian with the Latin alphabet. Under Mongolian and Turkish rulers, Persian was adopted as the language of government in Turkey, central Asia and India, where it was used for centuries, and until after 1900 in Kashmir.
Persian is a member of the Iranian branch of Indo-European languages spoken by about 130 million people, mainly in Iran, Afghanistan and Tajikistan. There are also significiant numbers of speakers in many other countries, including Uzbekistan, Bahrain, Iraq, Turkey, Kuwait, Azerbaijan, Israel, Turkmenistan, Oman, Yemen, the UAE and the USA. In Afghanistan Persian is known as Dari (درى) or Dari-Persian, while in Tajikistan it's known as Tajiki (Тоҷики / تاجيكى).
Persian, Farsi or Parsi?
The official language of Iran is sometimes called Farsi in English and other languages. This is a correct transliteration of the native name of the language, however many, including the ISO and the Academy of Persian Language and Literature, prefer the name Persian for the language. Some speakers use the older local name: Parsi (پارسی). There is some discussion about this topic at: www.iranian.com and wikipedia.
Iran or Persia?
Until 1935, the official name of the country currently known as Iran was Persia, though the Persian people have called their country Iran since the Sassanid period (226 - 651 AD). There's further discussion about this at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iran_naming_dispute
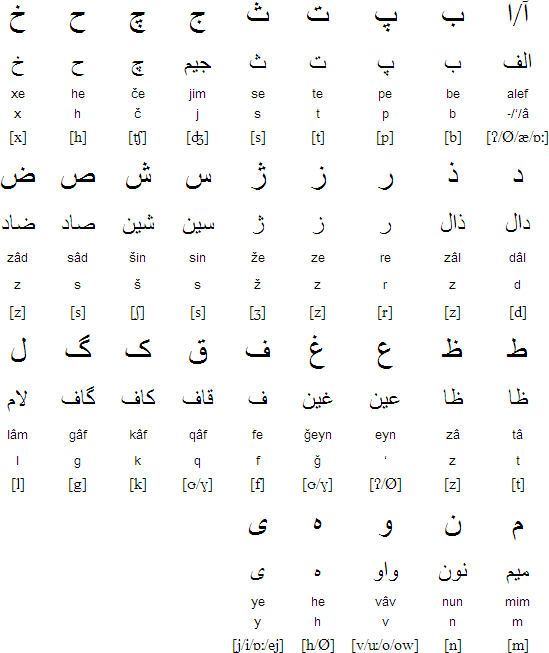
Persian alphabet (الفبای فارسی) and pronunciation
Notable features
Type of writing system: abjad - includes letters only for consonants. Vowels, when indicated, are written with diacritics and/or combinations of consonant letters
Direction of writing: right to left in horizontal lines; numerals written from left to right.
Used to write: Persian (فارسی)
Persian alphabet and pronunciation
Persian has six vowel sounds and two diphthongs: â (/ɒː/), a (/æ/), e (/e/), I (/iː/), o (/o/), u (/uː/), ey (/ej/) and ow (/ow/).
"Alef" has no particular sound. At the beginning of words by means of diacritics it can denote "â" (آ), "a" (اَ), "e" (اِ), "o" (اُ) but elsewhere, it always denotes "â". However, only the diacritic of "â" (آ) is commonly written and you just have to memorize the pronunciation. For example: آب (âb) – water, اسب (asb) – horse, امید (omid) – hope, امشب (emšab) - tonight.
Notes and corrections by Ali Jahanshiri
Numerals
Persian numerals
The symbols for 4,5 and 6 are different from the standard numerals used for Arabic.
Sample text
Sample text in Persian
Transliteration (from Ali Jahânshiri)
Tamâm-e afrâd-e bašar âzâd be donyâ miâyand va az lehâz-e heysiyat-o hoquq bâ ham barâbar-and. Hame dârâ-ye aql-o vejdân mibâšand va bâyad nesbat be yekdigar bâ ruh-e barâdari raftâr konand.
Translation
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
Information about Persian | Persian phrases | Persian numbers | Tower of Babel in Persian | Persian learning materials
Iranian languages
Avestan, Baluchi, Bartangi, Dari, Gilaki, Ishkashimi, Juhuri, Khufi, Kurdish, Luri, Mazandarani, Ossetian, Oroshor, Persian, Parthian, Pashto, Rushani, Sanglechi, Sarikoli, Shabaki, Shughni, Tajik, Talysh, Tat, Wakhi, Yaghnobi, Zazaki
Persian phonetic keyboard layout is for Microsoft Windows users interested to profit from their skill in typing with Latin QWERTY keyboards (English, Spanish, French, German, ...) to type Persian characters much faster. Persian phonetic keyboard layout can be installed on Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8. As far as possible, Persian characters are ordered in a way that by typing a Latin key you can get its Persian equivalent. For example, by typing "L" you get ل. Regarding sounds that have several characters in Persian alphabet (e.g. S's, Z's), the most frequent character is available on the normal state of the keyboard and the other homophone characters are available on the Shift state next to the first key. For example, by pressing "S" key, you get س. For typing ص and ث, you must first hold Shift key down and then press "S" and "D" respectively. ZWNJ stands for zero-width non-joiner. It's named so because it makes its preceding character appear in its non-joining form. For example, if you put ZWNJ after ی in میروم it changes to میروم. As you see, ZWNJ itself isn't visible but we can detect it from its effect on its preceding character. ZWJ stands for zero-width joiner. It's named so because it makes its preceding character appear in its joining form. For example, if you put ZWJ after ی it changes to ی. Just like ZWNJ, ZWNJ itself isn't visible but we can detect it from its effect on its preceding character.
Frontype is easy to use multilingual user-friendly virtual onscreen keyboard that turns any keyboard to your language layout. Just add needed language as input and start to type!
 Farsi
Farsi
FARSI DESKTOP KEYBOARD FREE DOWNLOAD
Farsi (Persian)Farsi belongs to Iranian branch of Indo-European language family. Persian or Western Farsi isspoken by about 22 million people residing in Iran. A close variant, Dari (Eastern Farsi), isspoken by seven million people in Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan. Both varieties are also spokenin some other countries as well [1, 2]. Figure 1 shows the language family tree of Farsi.Indo-EuropeanIndo-IranianIranianWesternSouth WesternPersianFARSI Lan..
$0.00

Persian, Fārsi, is a member of the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family. It is a macrolanguage spoken by an estimated 110 million people worldwide, primarily in Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan. The language is known by several names. Persian is the more widely used name of the language in English, from Latin Persia, from Greek Persis. The Academy of Persian Language and Literature calls the language Persian. Farsi is the Arabicized form of Parsi, from Pars, the name of the region where the language evolved. Pars is called Fars in Arabic which lacks the sound [p]. Dari is the local name used for Persian in Afghanistan. Tajik (Tajiki) is the local name used for Persian in Tajikistan.
StatusPersian enjoys official status in three countries.
-
Iran
Western Persian (New Persian, Parsi, Persian) is spoken as a 1st language by 45 million people in Iran, a multilingual country, out of a total population of 81 million. It is the official language of Iran (Ethnologue). It is also spoken in Iraq, Oman, Qatar, and Tajikistan. Standard Persian is based on the dialect spoken in and around Teheran, the capital of Iran. -
Afghanistan
Eastern Persian (Dari, Afghan Persian, East Farsi) is the first language of about 7.6 million people in Afghanistan, the Khorasan Province of Iran, and in Pakistan (Ethnologue). It is the co-official language of Afghanistan, along with Pashto.Dari is Afghanistan’s lingua franca and is the native tongue of various Afghan ethnic groups -
Tajikistan
Tajiki (Galcha, Tadzhik, Tajik, Tajiki Persian, Tojiki) is spoken by 4.5 million people primarily in the Tajikistan and Uzbekistan, former Soviet republics in Central Asia (Ethnologue). Tajiki is the official language of Tajikistan. It is also spoken in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and
Click on the MLA Interactive Language Map to find out where Persian is spoken in the U.S.
Dialects
Ethnologue lists some 20 dialects of Persian that are usually divided into three major mutually intelligible groups whose treatment as separate languages is primarily based on geopolitical considerations. The three groups have diverged in their sound systems, and to some extent, in their structure and vocabulary, the latter showing differential influences of Arabic (in Iran), Pashto (in Afghanistan), and Russian (in Tajikistan). However, the literary language is virtually identical in Iran and Afghanistan, exhibiting only very minor differences.
Structure
Sound systemThe sound system of Standard Persian has 29 phonemes, i.e., sounds that make a difference in word meaning. The description below is based on the speech of educated people in Teheran.
Vowels
Persian has six vowel phonemes which are given below.
|
Front
|
Central
|
Back
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Close |
i
|
u
|
|
| Close-Mid |
e
|
o
|
|
| Near-Open |
æ
|
||
| Open |
a
|
- /æ/ = a in cat
Consonants
Persian has 23 consonant phonemes.
|
Bilabial
|
Labio-
dental |
Alveolar
|
Post-alveolar
|
Palatal
|
Velar
|
Uvular
|
Glottal
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stops | voiceless | p | t | k | |||||
| voiced | b | d | g | ||||||
| Fricatives | voiceless | f | s |
ʃ
|
x | h | |||
| voiced | v | z |
ʒ
|
ɣ | |||||
| Affricate | voiceless |
tʃ
|
|||||||
| voiced |
dʒ
|
||||||||
| Nasal | m |
n.
|
|||||||
| Lateral | l | ||||||||
| Rhotic | r | ||||||||
| Approximant | j |
- /x/ has no equivalent in English; similar to German pronunciation of ch in Bach
- /ʃ/ =sh in shape
- /ʒ/ = s in measure;
- /tʃ/ = ch in chat
- /dʒ/ = j in jet
- /j/ = y in yet
Stress
Stress typically falls on the last syllable of the root.
The grammatical systems of Farsi (Western) Persian and Dari (Eastern) Persian do not differ in any significant way. The description below covers the main grammar points of both languages. Both Dari and Farsi are inflected languages, i.e., they add suffixes to roots to express grammatical relations and to form words. Unlike many other Iranian languages, Dari and Farsi have lost most of their noun and verb inflections.
Nouns
- Nouns can be simple or compound.
- Any unmodified noun in Persian may be generic, i.e., refer to one or more than one items. Plural is not obligatory when more than one item are implied. The marker –hā signals plural with count nouns, e.g., ketāb-hā ‘books’, and amplification with mass nouns, e.g., āb-hā ‘all kinds of water, lots of water’. Human nouns take –ān, while nouns borrowed from Arabic usually take -in. Adjectives are not marked for number. Some nouns borrowed from Arabic can be pluralized by using the Arabic broken plural.
- There are no articles.
- There is no grammatical gender.
- Case is not marked.
- Persian distinguishes between genericity and indefiniteness. This applies to both count and mass nouns. It is expressed by the suffix –i, e.g., ketāb-i‘ ‘some/a book’, ketāb-hā ‘some books’. Definiteness is not marked formally.
- Possession is marked by the particle –e, e.g., ketāb-e Ali ‘the book of Ali’. Modifiers are also connected to the noun modified by the particle -e.
Verbs
Persian verbs are marked for the following categories:
- There are three persons: first, second, and third.
- There are two numbers: singular, and plural.
- There are three moods: indicative, subjunctive, counterfactual conditional.
- Aspect is as important as tense. There are two aspects: imperfective and perfective.
- There are three tenses: present, past, and inferential past. Inferential past expresses second-hand knowledge, information, or conclusions.
- Causality is marked by the suffix –ān, e.g., xor ‘to eat’ – xorān ‘to feed’.
- Future is not a tense but a modality (similar to the English want to/wanna + infinitive). All present and past forms may be used in a future context.
- Subject pronouns are usually dropped since the verb form already carries information about person and number.
Word order
The normal word order in Persian is Subject-Object-Verb. Modifiers follow the nouns they modify.
New words are formed from nouns, adjectives and verbal stems through derivation and compounding. In addition, Persian contains a large number of Arabic loan words. They are more common in the written than in the spoken language. Since the beginning of the 20th century, Farsi, Dari,and Tajik have experienced different influences on their vocabulary. Pashto words have been introduced into Dari in Afghanistan, and a large number of Russian words has entered Tajik in Tajikistan. Farsi has borrowed a significant number of words from French, German, and most recently from English, especially in science and technology.
Below are a few common Persian phrases and words given in romanization.
| Hello | Salām. |
| Peace be with you. | Salām aleikom. |
| Good bye | Xodāfez. |
| Please. | Lotfān. |
| Thank you. | Tashakor. |
| God willing. | Enshā ‘allah. |
| Excuse me. | Bebaxshīd. |
| Yes | Bale |
| No | Na |
| Man | Mard |
| Woman | Zan |
Below are the Persian numerals 0-9.
۰ ۱ ۲ ۳ ۴ ۵ ۶ ۷ ۸ ۹
| . | ۱ | ۲ | ۳ | ۴ | ۵ | ۶ | ۷ | ۸ | ۹ | |
| sefr | yek | do | se | chahār | panj | shesh | haft | hasht | no |
Writing
The bulk of the surviving Persian literature comes from the times following the Islamic conquest of Iran in the 7th-8th centuries AD when the Persians, who wrote in both Persian and Arabic, became the scribes and bureaucrats, as well as writers and poets, of the Islamic empire. Persian poets such as Saadi, Hafez, Omar Khayyam and Rumi have left a significant mark on the literature of many countries.
Persian and Dari are written in the Perso-Arabic script, which contains additional letters to represent Persian sounds [p], [ʃ], [ʒ], [g], not represented in the Arabic alphabet. The alphabet is basically consonant-based. Like Arabic, it is written from right to left. Tajik uses a modified Cyrillic alphabet.
In recent years, efforts have been made to introduce alternative alphabets for writing Persian. One such proposed alphabet is UniPers which is given below.
|
A a
|
 â
|
B b
|
C c
|
D d
|
E e
|
F f
|
G g
|
H h
|
I i
|
J j
|
K k
|
L l
|
M m
|
N n
|
|
O o
|
P p
|
Q q
|
R r
|
S s
|
Š š
|
T t
|
U u
|
V v
|
W w
|
X x
|
Y y
|
Z z
|
Ž ž
|
Take a look Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in the Perso-Arabic script and in the Latin script.
|
|
| Tæmam e æfrad e bæscær azad be donja mi ajænd o æz læhaz e hejsijæt o hoghugh ba hæm bærabær ænd. Hæme dara je æghl o vedjan mi bascænd o bajæd nesbæt be jek digær ba ruh e bradæri ræftar konænd. |
| All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood. |
English has borrowed a number of words from Persian. Persian, in turn, borrowed many of these words from Arabic. Most of them came into English indirectly through other languages, mostly French and Greek. A few of them are listed below:
|
English word
|
from Persian
|
|---|---|
| baksheesh | bakhshish, literally ‘gift’ |
| bazaar | bazar ‘market’ |
| caravan | karwan ‘group of desert travelers’ |
| caviar | khaviyar, from khaya ‘egg’ + dar ‘bearing’ |
| lac | lak ‘resinous substance’ |
| magic | Old Persian magush ‘magician’ |
| mummy | mumiya, from mum ‘wax’ |
| pilaf | pilaw, a rice dish with meat |
| pistachio | pista ‘pistachio tree’ |
| shah | shah, title of king of Persia |
| scarlet | saqirlat, a kind of rich cloth, not necessarily red |
| seersucker | shir-o-shakkar ‘striped cloth’, literally ‘milk and sugar’, an allusion to the alternately smooth and puckered surfaces of the stripes; from shir ‘milk’ + ‘hakar ‘sugar’ |